√70以上 greenhouse effect diagram blank 164534-Greenhouse effect diagram blank
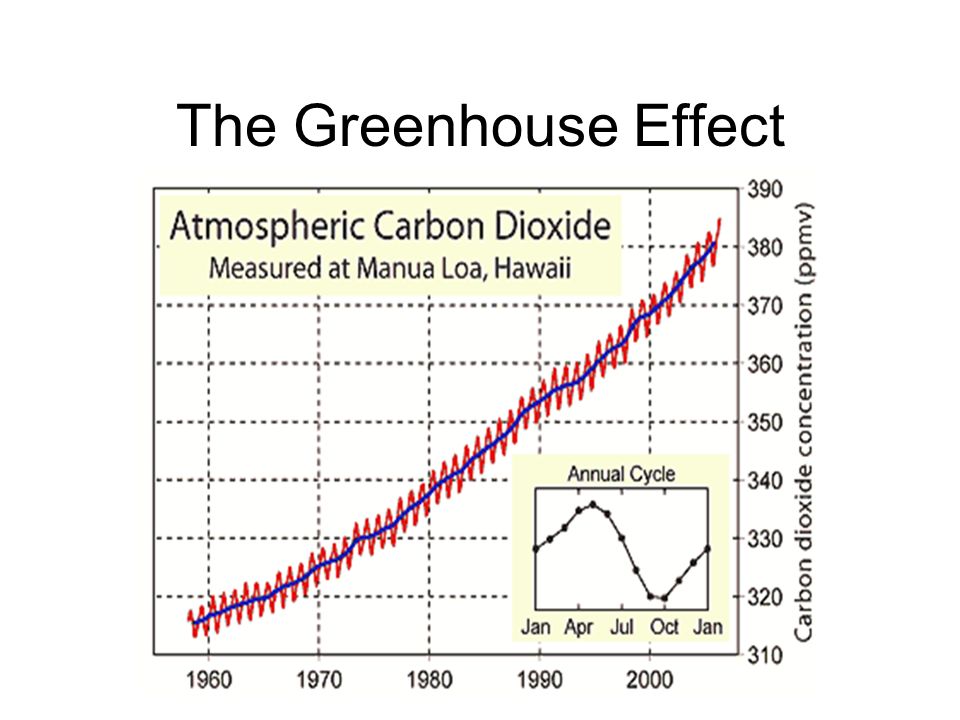
Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees CelsiusFind the perfect Greenhouse Effect Diagram stock photos and editorial news pictures from Getty Images Select from premium Greenhouse Effect Diagram of the highest qualityBrowse 6,474 greenhouse effect stock illustrations and vector graphics available royaltyfree, or search for greenhouse effect diagram or greenhouse effect illustration to find more great stock images and vector art
Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse effect diagram blank
Greenhouse effect diagram blank- The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part ofAlso methane, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Possible implications of increased greenhouse effect Junior Cycle Science Earth and space Sustainability 3



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
(b) On the figure you selected, CIRCLE the part of the diagram which represents the energy processes DIRECTLY involved in the greenhouse effect (c) Explain WHY the figure you selected is a more accurate depiction of the natural Greenhouse Effect than the other two figuresMake a Garden Lampshade Birds and Climate Change Do a science fair project!Teaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsaligned activities, content, and multimedia that build
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans There is strong evidence that recent changes are unprecedented and not due to natural Greenhouse Atmosphere Let's Heat Things Up!The greenhouse effect is the process thanks to which Earth has a higher temperature than it would have without it The gases that radiate heat also known as greenhouse gases absorb the energy radiated out by the Earth and reflect a part of it back to Earth Of all the energy that the Earth receives from the Sun, a part of it around 26% is
Students observe teacherled demonstrations, and build and evaluate simple models to understand the greenhouse effect, the role of increased greenhouse gas concentration in global warming, and the implications of global warming for engineers, themselves and the Earth In an associated literacy activMake an Ocean Ecosystem Dessert Meet the Greenhouse Gases!Make a terrarium minigarden Make S'Mores With a Solar Oven!



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Activities Make a NASA Climate Kids Pumpkin!Greenhouse gases diagrams • Where do Greenhouse Gases Come From handouts • Greenhouse Gas Emissions Diagram handouts • Colored pencils National Science Education Standards D1h The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases that include water vaporThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect Gizmo Lesson Info Explorelearning
The greenhouse effect of Venus From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux over the surface of Venus It is approximately 661 W/m2 Venus is very reflective of solar radiation In fact, it has a reflectivity (or albedo) of 08, so the planet absorbs approximately 661 X 02 = 132 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals theAlthough the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouse The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight



Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature
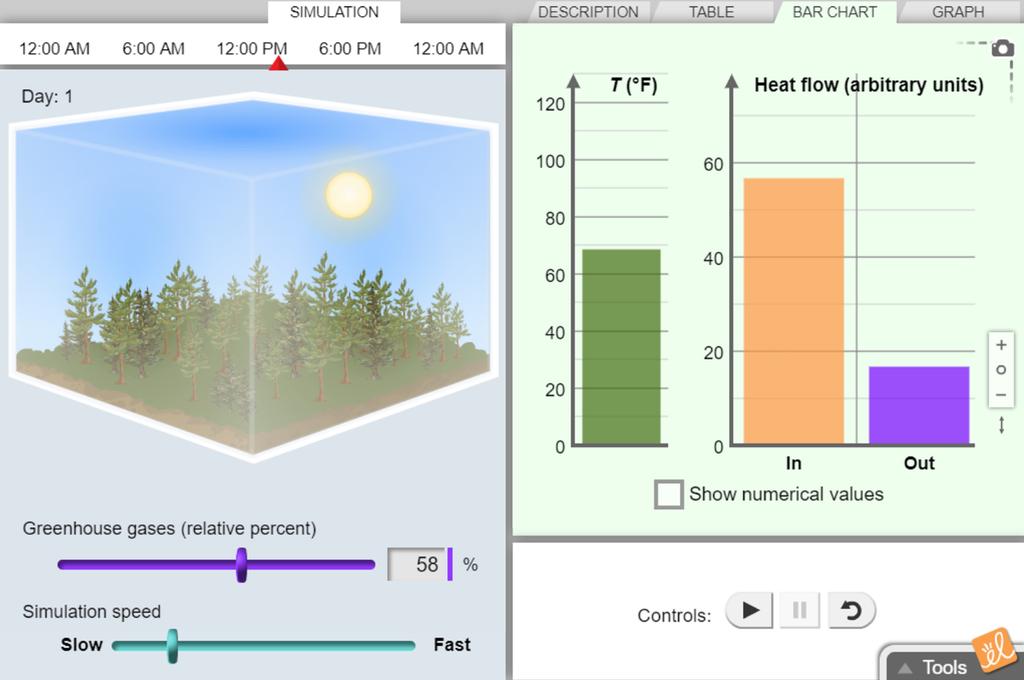
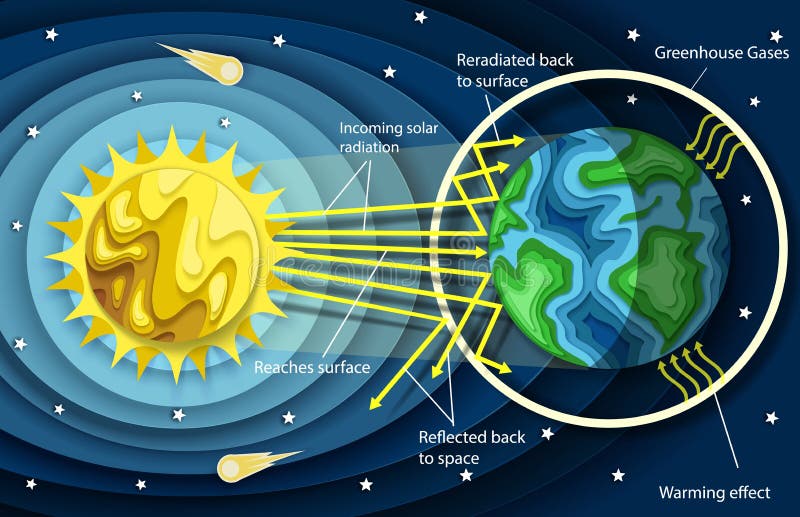
The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmospherePhET The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Tab In this final part of Part 1, you'll take a step back and view the process of the Greenhouse Effect as a whole On the PhET website linked at the top of this lab page, click on the 'Greenhouse Effect' tab Read below for details on the use of this simulation from the University of Colorado The Greenhouse Effect Life in a greenhouse?




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Small Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Full Size Png Download Seekpng
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16° F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearlyIn bright sunshine, the air inside a greenhouse becomes warm The greenhouse glass lets in the sun's light energy and some of its heat energy This heat builds up inside theGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effect




Clipart Resolution 2400 1768 Blank Greenhouse Effect Diagram Transparent Png 900x663 Free Download On Nicepng




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences theWrap one in a plastic bag (this is the greenhouse glass) Leave both jars in the sun for one hour Measure the temperature of the water in each jar What you'll discover!The "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works



Www Reefrelief Org Wp Content Uploads Climate Greenhouse2 Pdf




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
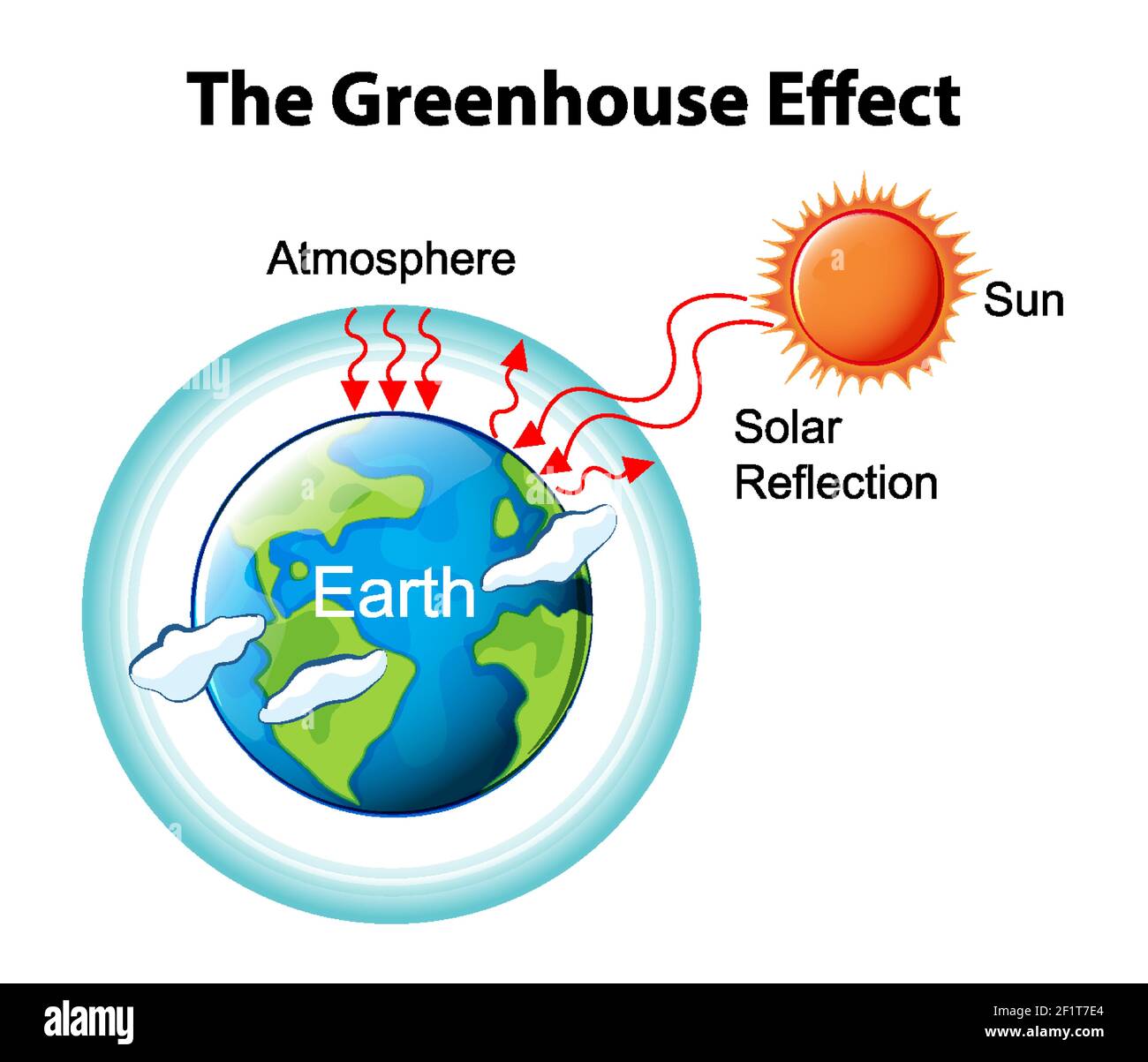
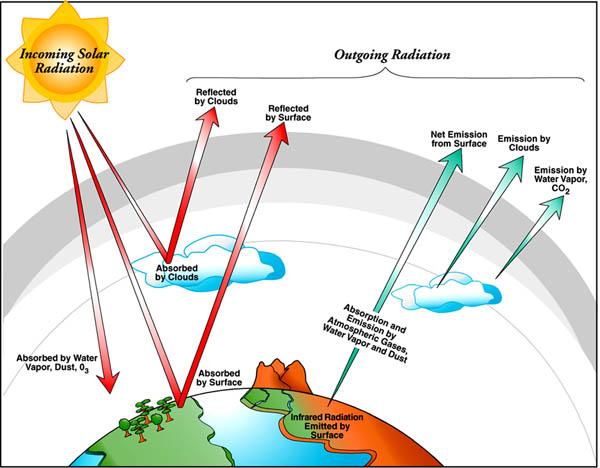
Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature aboveGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinatedThe greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space Energy emitted from the sun ("solar radiation") is concentrated in a region of short




Download Ecological Illustration Depletion Of The Ozone Layer Ozone Hole Man With An Umbrella Covers Planet Earth From Eff In 21 Eco City Ozone Layer Ozone Hole




The Greenhouse Effect Worksheet Answers Worksheet List
Observe the Greenhouse Effect in a Jar This experiment gets kids exploring how a greenhouse works, and in turn how greenhouse gases affect the Earth's atmosphere Your child will strengthen observation and recording skills, work with a control, and draw conclusions And bonus this is a great outdoor activity!CHAPTER 7 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT We examine in this chapter the role played by atmospheric gases in controlling the temperature of the Earth The main source of heat to the Earth is solar energy, which is transmitted from the Sun to the Earth by radiation and is converted to heat at the Earth's surface Greenhouse effect diagram can either be printed off or projected and used to explain the Greenhouse effect



Static1 Squarespace Com Static 58acfc0e092fdb01e T 58bec0fbe3dfe3365c Lesson 2 Greenhouse Effect Lesson Plan Pdf



Www Explorelearning Com Index Cfm Method Cresource Dspview Resourceid 372
A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warmActivity 12 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 5 – 6 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will complete a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion questions, and perform a skitIt is part of the thermosphere Mesosphere the atmospheric layer between the stratosphere




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
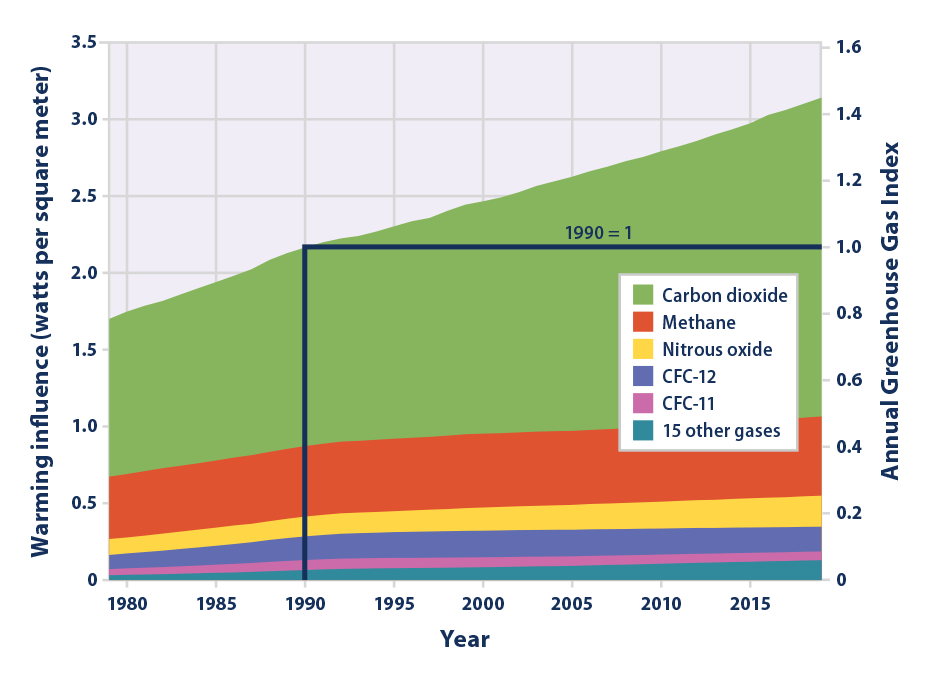
A greenhouse is for growing plants It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight But why not just put the plants outside? Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air2 Greenhouse Gases Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, followed by carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other trace gases 5 Carbon dioxide is the second most abundant greenhouse gas and it absorbs radiant energy (heat) Therefore, when the CO 2 concentration increases, so does atmospheric temperature 3 Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases in



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount ofFinally, finish reading Life in the Greenhouse Explain Explain to students that they will create a diagram (an infographic) showing how the greenhouse effect works First, they will examine books (and online sources of information, if desired) to learn more about the greenhouse effect and view sample infographicsThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouse



Greenhouse Effect Blank Diagram Clip Art Library




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate
Guest post by Kevin Judd Climate scientists are telling us that gases like carbon dioxide are causing global warming Carbon dioxide is produced when petrol is burned in your car engine, or when coal and gas are burned at powerstations to make electricity Carbon dioxide causes global warming because it contributes to the socalled greenhouse effectOff the surface is absorbed and reradiated into the atmosphere, where much of it is absorbed by the greenhouse gases This is known as the greenhouse effect BACKGROUND Use the following terms to label the diagram belowThis information sheet outlines the major requirements and factors that should be considered by someone contemplating starting a small greenhouse operation for the production of annuals, potted plants, vegetables, nursery stock, perennials, herbs or other specialized crops It can also be used when planning the expansion of an existing business




Earth S Energy Budget And Greenhouse Effect By Beakers And Ink Tpt



1
Label the layers of the Earth's atmosphere using the terms below Exosphere the outermost layer of the Earth's atmosphere, where atmospheric pressure and temperature are low Ionosphere the atmospheric layer between the mesosphere and the exosphere;The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist docx, 709 KB Fill in the blanks about the greenhouse effect, which is thought to be a cause of climate change Included is an answer sheet, a higher ability sheet with limited clues, and a lower ability sheet with less complicated language and more clues Tes classic free licence



Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate




Zoona Ibrahim Greenhouse Effect
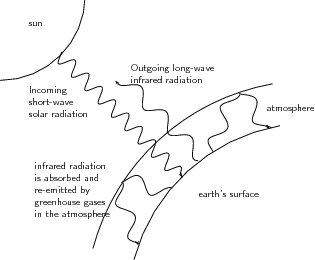
The Natural Greenhouse Effect Just as the major atmospheric gases (oxygen and nitrogen) are transparent to incoming sunlight, they are also transparent to outgoing thermal infrared However, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and other trace gases are opaque to many wavelengths of thermal infrared energyGreenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice!The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory




A Natural Greenhouse Effect B Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
Form definitions of the greenhouse effect based on prior knowledge, class discussion, and viewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientificThe greenhouse effect and the influence of human activity on it Greenhouse gases and their relative effects especially carbon dioxide and water vapour; Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to




The Greenhouse Effect World101




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
The greenhouse effect is a good thing It warms the planet to its comfortable average of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius) andThe Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planetA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3) Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 1 Understandingthegreenhouseeffect Pdf




The Greenhouse Effect It Is Necessary And Natural Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




File Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons




画像 Greenhouse Effect Diagram ちょうど最高の引用




Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Worksheet



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



Top Of Greenhouse Effect Diagram Black And White Annejeannne



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature
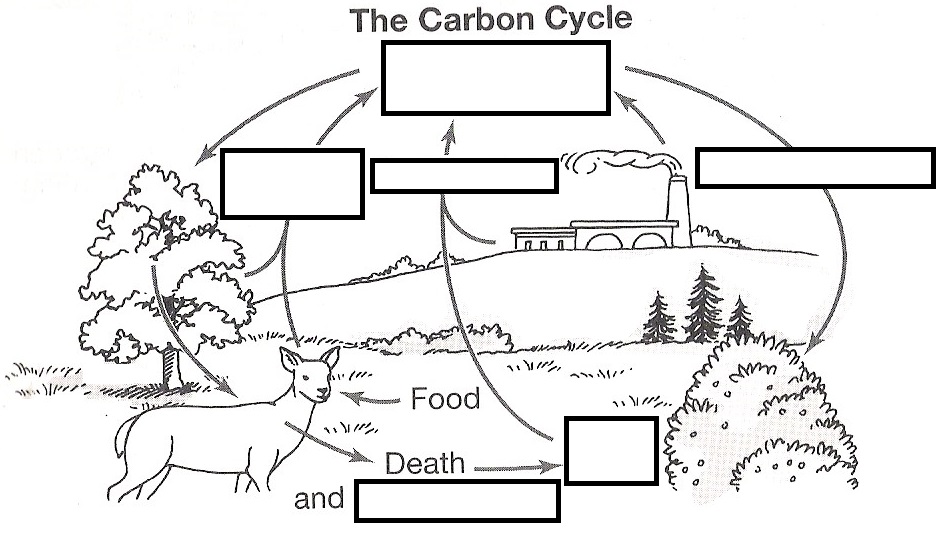



Copy Of The Carbon Cycle Interactive Worksheet By Ladi Oyediran Wizer Me




Activity 2 Show Your Understanding Of The Greenhouse Chegg Com




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




What Are They Singapore Energy Sustainability
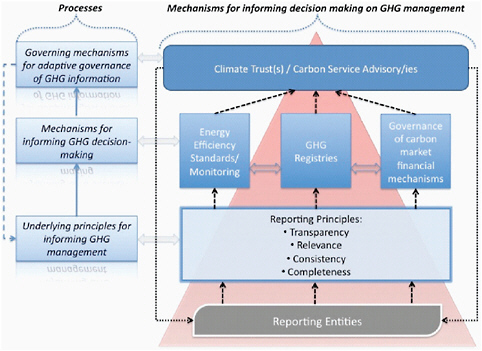



6 Informing Greenhouse Gas Management Informing An Effective Response To Climate Change The National Academies Press




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
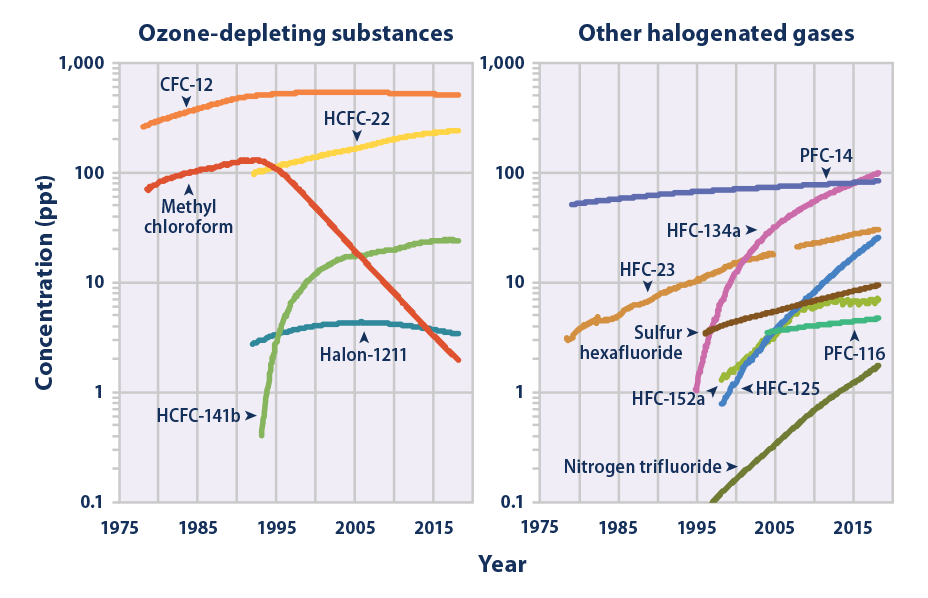



Youxclg0bikhtm




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



Al Gore And Bill Nye Fail At Doing A Simple Co2 Experiment Watts Up With That




Diagram Fill In The Blanks Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas



The Greenhouse Effect
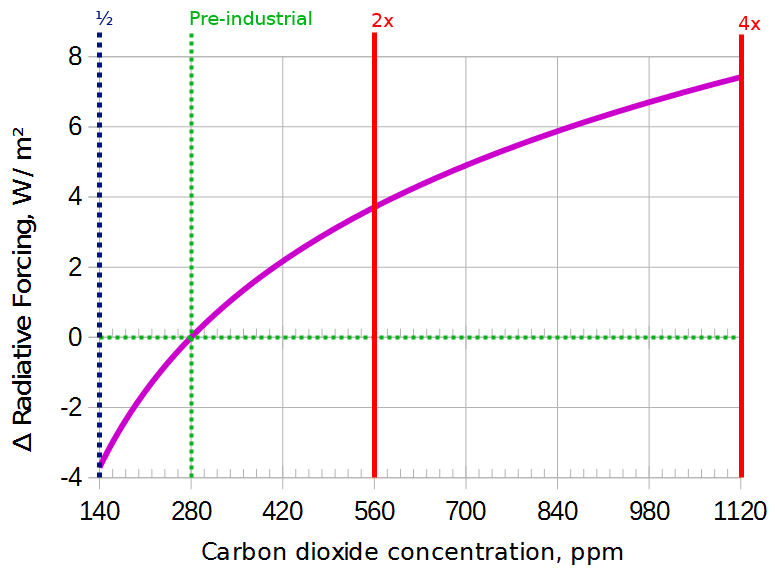



How Could Global Warming Accelerate If Co2 Is Logarithmic



Www Lordgrey Org Uk F014 Usefulresources Aric Resources Teaching Packs Key Stage 3 Global Warming Pdf Global Warming Pdf



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Green House Drawing For Kids Novocom Top




Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Worksheet




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Q Tbn And9gcqh0jupg3p Zz6lfbc5xhscznxwfk4ldvqaetml Nqvnvmx8swv Usqp Cau




Green House Effect In Hindi ग र न ह उस इफ क ट Youtube



Greenhouse Effect Clip Art At Clker Com Vector Clip Art Online Royalty Free Public Domain



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




The Greenhouse Effect 6 E 2a 2 What Is A Green House A Greenhouse Is Made Of Glass It Traps The Sun S Energy Inside And Keeps The Plants Warm Even Ppt Download




Effect Of Clay On Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Humification During Pig Manure Composting As Supported By Spectroscopic Evidence Sciencedirect



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




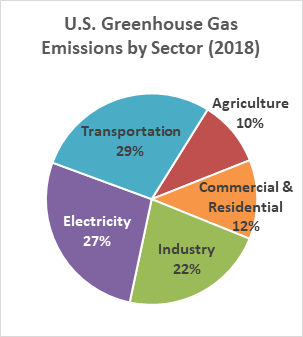
Uk Ghg Emissions Shares By Sector 19 Statista



8th Grade Science Jh Science Technology



Www Manhassetschools Org Cms Lib8 Ny Centricity Domain 709 Greenhouse student Pdf




The Diagram Given Shows The Green House Effect Which Of The Following Would Have Been In The Absence Of Greenhouse Effect In The Atmosphere



Kenl Qwhyysavm




Fishbone Diagram For Thesis Cause And Effect Diagram For Students Transparent Png 1346x985 Free Download On Nicepng




Let Us Trynow That You Have Read And Discovered Things About The Greenhouse Effect Try Thewrite A Brainly Ph



Free Greenhouse Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library



Q Tbn And9gcsuarho6zcojihci37ad2wcnqvuhx4bdek5loexq0y1ocgx8dab Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Effect Colorado New York Amy Shackleton




Carmen Faczek Carmenfaczek Profile Pinterest



Untitled Document



Lab 2 Climate And Earth S Energy Balance



The Greenhouse Effect




Effects Of Microplastics On Greenhouse Gas Emissions And The Microbial Community In Fertilized Soil Sciencedirect




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet



Www Manhassetschools Org Cms Lib8 Ny Centricity Domain 709 Greenhouse student Pdf



The Greenhouse Effect
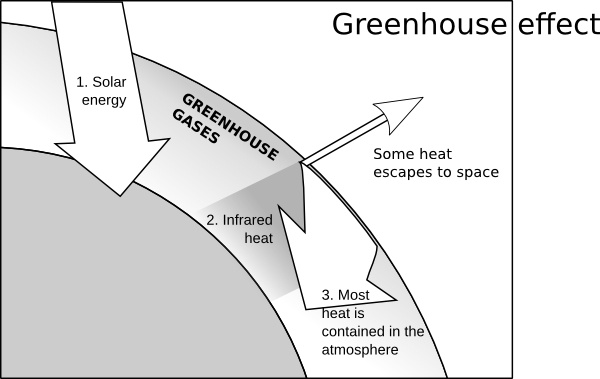



Capjerimum Greenhouse Effect Clip Art Free Vector In Open Office Drawing Svg Svg Vector Illustration Graphic Art Design Format Format For Free Download 448 42kb



Wow Teaching Science Through The Greenhouse Effect 7




The Greenhouse Effect World101



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Free Online Fishbone Diagram Maker Design A Custom Fishbone Diagram In Canva



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Effect Svg Vector Greenhouse Effect Clip Art Svg Clipart



Static1 Squarespace Com Static 58acfc0e092fdb01e T 58bec0fbe3dfe3365c Lesson 2 Greenhouse Effect Lesson Plan Pdf




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
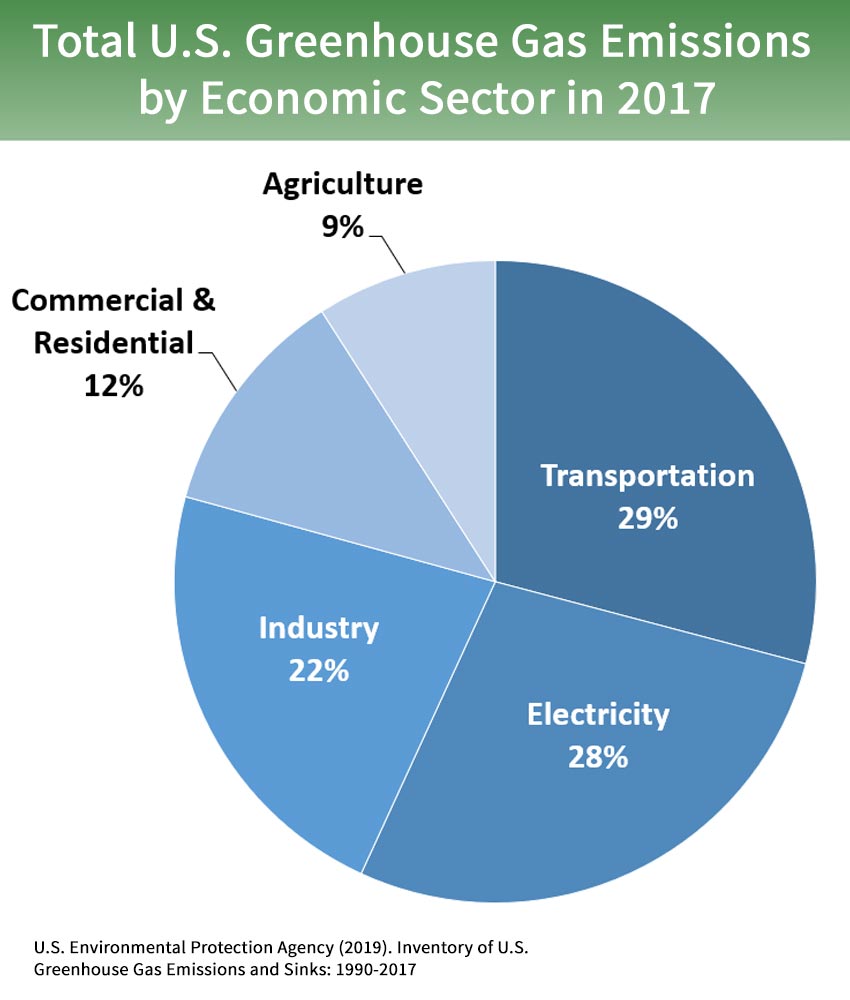



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector U S 17 Blank Template Imgflip




Free Online Fishbone Diagram Maker Design A Custom Fishbone Diagram In Canva
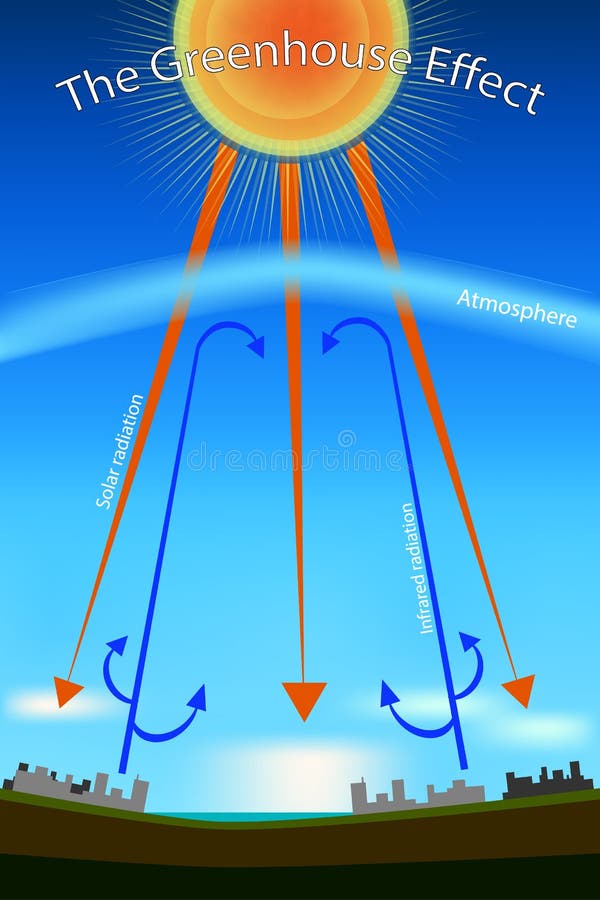



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
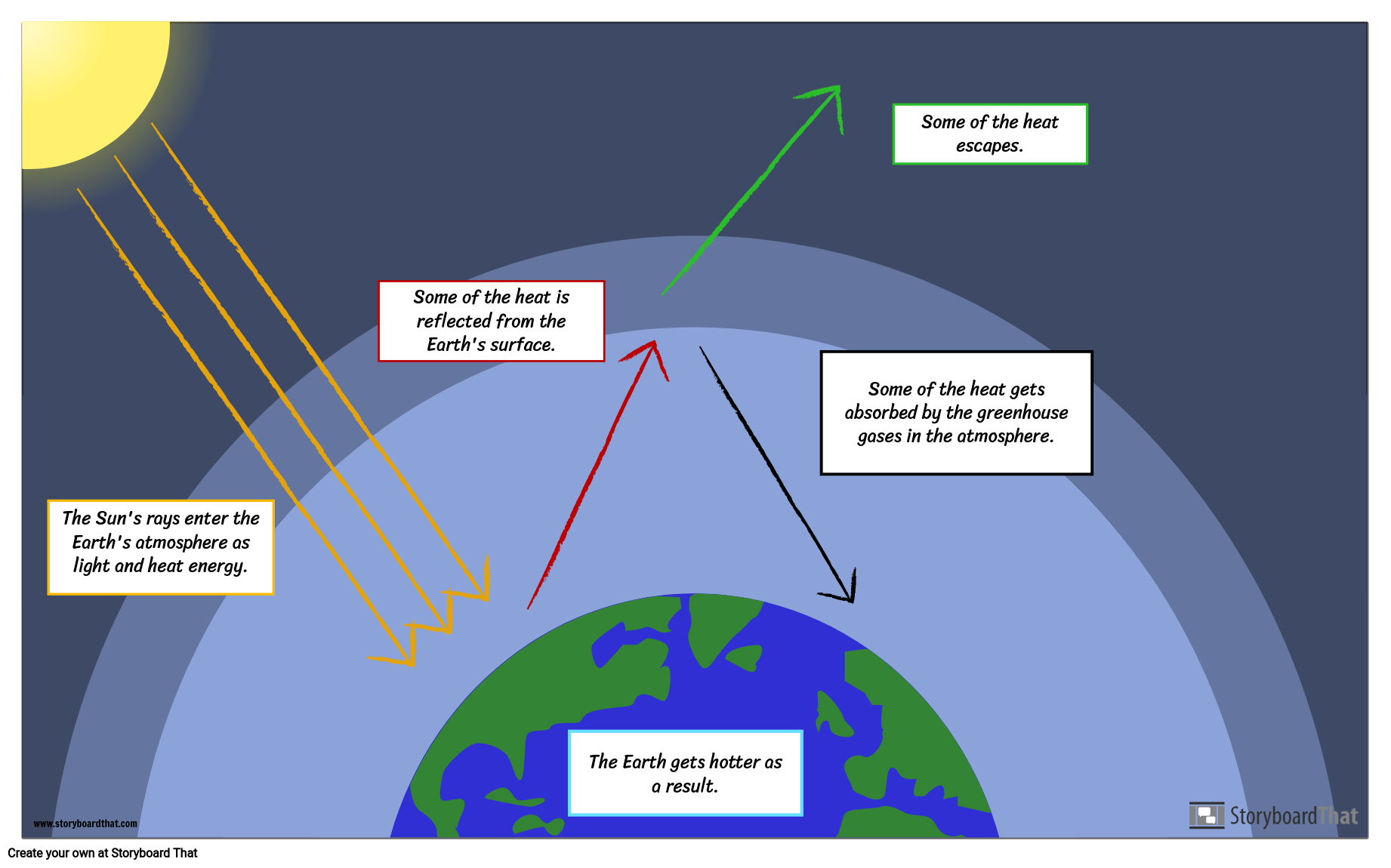



The Greenhouse Effect Worksheet Worksheet List



1



コメント
コメントを投稿